

In Dubai, non-resident companies often face challenges navigating complex accounting and tax regulations. Dubai accounting firms provide essential support to foreign businesses and individuals by managing financial obligations while conducting operations in the emirate. These firms play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with UAE tax laws, offering services ranging from obtaining a Tax Registration Number (TRN) to filing VAT returns. Their expertise is vital for foreign entities to meet their financial responsibilities in Dubai.
This guide outlines the key aspects of accounting and tax compliance for non-residents in Dubai and highlights how it has transformed and streamlined Dubai accounting practices.
Understanding Dubai accounting and tax compliance can be complex for businesses, especially those operating internationally. For both local and foreign entities, adhering to UAE regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations. Our Dubai Accounting Services are designed to help businesses comply with local requirements, covering everything from TRN registration to filing VAT returns.
Whether you're a non-resident company expanding into Dubai or an established entity, our tailored accounting solutions simplify compliance. We handle financial reporting, statutory bookkeeping, and VAT filings, ensuring that your business stays compliant with UAE laws while maximizing potential benefits like the UAE's tax-friendly environment.
Our Dubai accounting services are designed to maximize your profits by ensuring compliance and financial efficiency. Whether you're operating within the GCC or expanding into non-GCC markets, we focus on Dubai as the central hub for expert financial management.
With tailored solutions, we handle everything from TRN registration to VAT filings, helping your business meet regulatory requirements while reducing operational costs. This allows you to focus on growth while we take care of the financial intricacies.
Dubai accounting regulations are governed by a robust framework designed to ensure transparency, accuracy, and compliance for both local and foreign businesses operating in the UAE. Key regulations include:
Businesses must maintain detailed records of all financial transactions and prepare their accounts according to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). VAT compliance is essential, with regular filings required for both domestic and international transactions.
By adhering to Dubai accounting regulations, companies can ensure smooth operations, avoid legal issues, and benefit from the UAE's favorable tax environment.
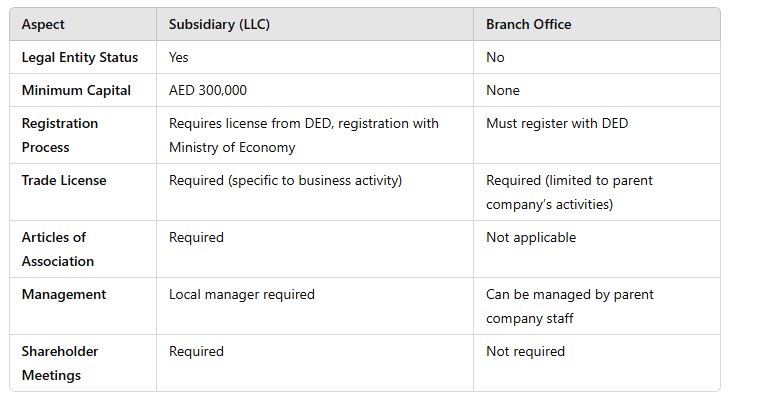
When expanding globally, including into Dubai, understanding legal entity types is crucial. We offer comprehensive Entity Management services to guide non-residents through selecting the right structure for their business needs.
In Dubai, non-residents can choose from several legal entity types, such as:
Each has different requirements and benefits based on the scale and nature of your business.
Registering a branch office in Dubai impacts your accounting practices significantly. As part of our global entity management services, we guide you through these changes to ensure compliance and efficiency.
Your branch office must adhere to UAE accounting standards, which include maintaining detailed financial records and preparing regular VAT returns. This requirement helps in ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance.
Tax registration in Dubai is crucial for businesses, including those from non-EU countries. Registering with the relevant tax authorities ensures compliance and facilitates smooth operations within Dubai and beyond.
VAT for Businesses with VAT-Taxable Transactions
Businesses involved in VAT-taxable transactions must obtain a VAT number. This registration allows companies to collect VAT on sales and claim VAT on purchases, aligning with Dubai’s VAT laws. Accurate VAT reporting and timely submissions are essential to avoid penalties.
Global Entity Management Services
Our global entity management services focus on helping businesses navigate Dubai’s tax regulations, including VAT requirements. We support companies from both EU and non-EU countries in obtaining and managing their VAT registration, ensuring compliance and optimizing financial operations.
With our expertise, businesses can streamline their tax registration process and effectively handle VAT obligations, paving the way for successful operations in Dubai and worldwide.
To hire staff in Dubai, you must register as an employer with the relevant local authorities. This process ensures compliance with local payroll regulations and tax laws. Our global entity management services simplify this registration for businesses, including those from non-EU countries, with Dubai as our primary focus.
We handle the entire registration process, from submitting required documentation to managing ongoing payroll obligations. Our expertise ensures that you meet all legal requirements and avoid potential penalties.
With our support, you can efficiently manage payroll and tax deductions for your employees in Dubai. We provide a seamless experience, allowing you to focus on growing your business while we ensure compliance.
Our services extend worldwide, offering tailored solutions for businesses entering the Dubai market or managing staff across borders. Trust us to streamline your employer registration and payroll processes.
Understanding corporate tax liability is crucial for resident companies operating in Dubai. Our global entity management services focus on ensuring compliance with Dubai tax regulations while supporting businesses worldwide, including non-EU countries.
We handle all aspects of corporate tax liability, including accurate filing of returns and management of deductible expenses. Our expertise helps you navigate complex tax laws and optimize your tax position.
With Dubai as our primary area of focus, we ensure that your company meets all local tax requirements and takes advantage of available tax benefits. This comprehensive approach minimizes risk and maximizes financial efficiency.
Partnering with us provides peace of mind, knowing your corporate tax obligations are managed effectively while you focus on growing your business internationally.
For companies, whether resident or operating globally, including non-EU countries, financial statements must generally include:
A Balance Sheet: This document provides a snapshot of the company's financial position at a specific point in time, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity.
A Profit and Loss Account: Also known as the income statement, this account summarizes the company's revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specified period.
Notes to the Accounts: These notes provide additional context and detail to the financial statements, including accounting policies, methods, and other relevant information that enhances the understanding of the financial position.
These statements must accurately reflect the company's financial position, and the accounting principles used should be disclosed. Any changes to these principles must be justified and explained in the notes.
Parent companies must include financial data from "controlled subsidiaries" and other "group companies" in their consolidated financial statements. A "controlled subsidiary" is one where the company has more than 50% of the voting rights or can appoint or dismiss a majority of the directors.
In Dubai, consolidation may be waived if the subsidiary or group company qualifies as a small company under UAE law or if its financial information is included in the parent company’s consolidated statements prepared according to applicable UAE regulations.
For companies operating under Dubai regulations, including those with global operations and non-GCC subsidiaries, audit requirements are as follows:
Companies registered in mainland Dubai with an annual turnover exceeding AED 50 million are required to have their financial statements audited.
Free Zone companies may have different audit requirements based on their specific free zone regulations.
In Dubai, publication requirements for financial statements are less stringent compared to some other jurisdictions. However, certain entities may need to submit their financial statements to relevant authorities:

Public Joint Stock Companies (PJSCs) listed on local stock exchanges must publish their financial statements.
Free Zone companies may have specific publication requirements based on their free zone regulations.
For companies worldwide, including non-EU countries, annual accounts filing is a critical requirement. Our entity management services ensure that your company meets Dubai regulations by preparing and filing accurate annual financial statements.
We manage all aspects of the filing process, including the balance sheet, profit and loss account, and notes to the accounts, ensuring compliance with UAE accounting principles. This helps avoid penalties and maintain transparency.
Our services also cover consolidation requirements, ensuring that financial data from controlled subsidiaries and group companies is correctly included in your consolidated statements. We handle these requirements efficiently, regardless of your company's global presence.
Partnering with us guarantees that your annual accounts are filed on time and in accordance with Dubai laws, providing peace of mind as you focus on growing your business.
For companies, including those operating globally and in non-EU countries, audit requirements are critical. Medium and large entities, as well as those adopting IFRS, must have their annual financial statements audited by a qualified auditor in Dubai. This audit ensures compliance with UAE accounting standards and confirms the accuracy of the financial reports.
The auditor’s report must verify that the financial statements meet UAE accounting principles and accurately represent the company’s financial position. This requirement supports transparency and reliability in financial reporting, crucial for businesses operating across borders.
Non-resident entities operating in Dubai must comply with specific audit requirements based on their size and structure. According to the applicable UAE regulations, only medium and large companies, along with those applying International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), are mandated to have their annual financial statements audited by an independent, qualified auditor.
The determination of whether a company qualifies as medium or large is based on three key factors: the value of balance sheet assets, net turnover, and the number of employees. A company that meets at least two of these criteria for two consecutive years must undergo a mandatory audit. This ensures that the financial statements are accurate and adhere to UAE accounting standards.
The appointed auditor is responsible for providing a comprehensive report that includes an evaluation of whether the financial statements are in line with UAE accounting principles and whether they accurately represent the company’s financial position and results. Additionally, the auditor must confirm that the management board's report complies with legal requirements and that adequate additional information is provided.
Non-resident entities not subject to mandatory audits may still choose to undergo a voluntary audit. This can enhance the company’s credibility, assist in securing financing, and improve overall risk management and compliance. A voluntary audit is beneficial for making informed strategic decisions and maintaining a strong financial standing.
Alternatively, if a full audit is not necessary or desired, companies may opt for a review of their financial statements. This review provides a limited level of assurance, ensuring that the financial statements reflect the organization’s financial situation without the comprehensive assessment required in a full audit.
Foreign businesses operating in Dubai must navigate complex VAT compliance requirements. Our entity management services ensure you meet all necessary regulations, whether you are from within the GCC or a non-GCC country.
VAT Registration: To conduct business in Dubai, foreign entities must register for VAT. This process involves obtaining a UAE VAT number, which is essential for trading and invoicing within the country.
VAT Returns: Regular VAT returns must be filed to report sales and purchases. Our services handle these filings efficiently, ensuring timely and accurate submissions to avoid penalties.
Invoicing and Documentation: Proper invoicing and record-keeping are crucial for VAT compliance. We assist in maintaining accurate documentation, which supports your VAT claims and provides evidence in case of audits.
Cross-Border Transactions: For businesses involved in cross-border transactions, understanding the VAT implications is essential. We provide guidance on handling intra-GCC and non-GCC transactions, including VAT exemptions and reverse charges.
VAT Refunds: Foreign businesses may be eligible for VAT refunds on certain expenses. We manage the refund process, ensuring you claim back any VAT you're entitled to, which helps improve cash flow.
Compliance Audits: Regular compliance audits help identify and address potential issues before they become problems. Our services include periodic reviews to ensure ongoing adherence to UAE VAT regulations.
Changes in Regulations: VAT regulations can change frequently. We keep you informed about any updates or changes that may impact your VAT obligations, ensuring continuous compliance.
Expert Guidance: Navigating VAT requirements can be challenging. Our team of experts provides ongoing support and advice to help you understand and manage your VAT responsibilities effectively.
Non-resident entities operating in Dubai can choose between UAE GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) for preparing their financial statements. This choice affects how financial information is recognized, measured, presented, and disclosed.
UAE GAAP is influenced by the International Financial Reporting Standards but also incorporates specific local regulations and guidelines issued by the UAE Ministry of Economy and the UAE Accounting and Auditing Organization. It includes provisions relevant to entities operating within the UAE, ensuring compliance with local business practices and regulatory requirements.
IFRS, developed by the International Accounting Standards Board, offers a global framework for financial reporting and is widely accepted, providing several benefits:
Enhanced Comparability: IFRS makes it easier to compare financial statements across different countries and industries, benefiting investors and stakeholders.
Improved Transparency: IFRS demands more extensive disclosures than UAE GAAP, offering a clearer view of a company's financial position and performance.
Access to International Markets: IFRS can help entities access international capital markets, as many investors and lenders prefer or require it.
Transitioning from UAE GAAP to IFRS can be challenging and resource-intensive, but the benefits often outweigh the difficulties for companies looking to operate globally.
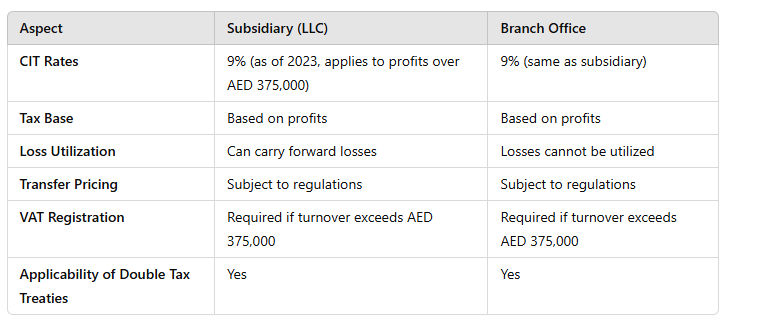
Dividends paid by UAE resident corporations are generally not subject to withholding tax, making the UAE an attractive destination for foreign investors. According to the UAE's tax regulations, there is currently no federal dividend withholding tax on profits distributed to shareholders.
However, companies should be aware of any specific regulations that may apply in certain Free Zones or as a result of international agreements. While the absence of a dividend withholding tax is a significant benefit, businesses should also ensure compliance with local regulations regarding the distribution of profits and potential documentation requirements.
Additionally, it is essential to consider any implications related to the tax residency of shareholders and any applicable tax treaties between the UAE and other jurisdictions, which may affect overall tax liabilities.
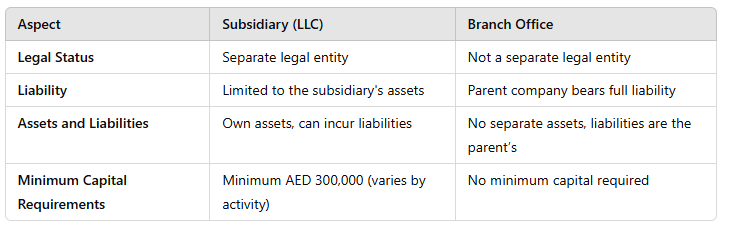
A foreign company with a branch in Dubai does not need to prepare separate UAE financial statements for the branch. However, a stand-alone balance sheet and profit and loss account may be required for tax purposes. Since a branch is not a separate legal entity from its head office, there are no withholding tax implications for transactions between the branch and the head office.
Parent companies are required to include the financial data of their "controlled subsidiaries" and other group companies in their consolidated financial statements. According to UAE law, a "controlled subsidiary" is defined as a legal entity where the parent company can either directly or indirectly exercise more than 50% of the voting rights at shareholder meetings or has the authority to appoint or dismiss more than half of the managing and supervisory directors.
When a parent company receives dividend payments from a subsidiary, these should be recorded as financial income in the profit and loss account. The amount due to be received should be listed as a receivable on the balance sheet until the payment is actually made.
For outgoing dividend payments to shareholders, these should be recorded as a reduction in retained earnings on the balance sheet. A corresponding liability should be recognized until the dividend payment is completed, in accordance with UAE accounting standards.
Under UAE law, specifically the Commercial Companies Law (Federal Law No. 2 of 2015), the board of directors must prepare the financial statements within three months of the end of the financial year. This period can be extended to a maximum of six months if approved by the shareholders at a general meeting due to exceptional circumstances.
The shareholders must then adopt the financial statements within two months of their preparation.
If the financial statements are not adopted within six months of the end of the financial year, the board of directors is required to notify the relevant authorities, including the Department of Economic Development (DED) or the relevant Free Zone Authority. This notification must include the reasons for the delay and the anticipated date of adoption.
Once the financial statements have been adopted, they must be filed with the relevant authorities, such as the Department of Economic Development (DED) or the applicable Free Zone Authority, within 30 days of adoption. The filing must include:
If the shareholders have not adopted the financial statements, the board of directors must still file the prepared financial statements within two months after the due date for adoption, accompanied by a statement indicating that the financial statements have not yet been adopted.
Failing to meet filing requirements can lead to penalties under the UAE Commercial Companies Law (Federal Law No. 2 of 2015). Board members may be personally liable for any damages caused to third parties due to non-compliance.
To avoid these penalties, non-resident entities should be mindful of annual reporting deadlines and filing requirements. It is also advisable to seek professional advice to ensure full compliance with UAE accounting regulations.
According to the UAE Commercial Companies Law (Federal Law No. 2 of 2015), the audit requirements for companies in Dubai are determined by their size category. The size criteria are based on three factors: the value of the balance sheet assets, net turnover, and the number of employees. If a company meets at least two out of the three criteria for a specific category in two consecutive years (or in the first year for newly formed companies), that category applies.
The table below summarizes the size criteria for each category:
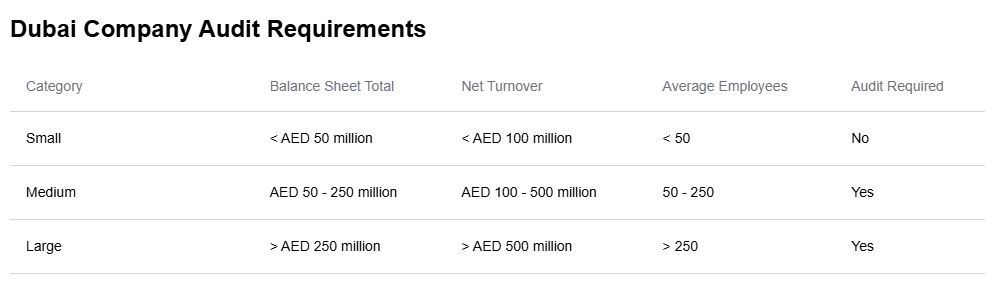
Under UAE law, only medium-sized and large companies are legally required to have their financial statements audited by an independent, qualified, and registered auditor recognized by the UAE.
Micro and small-sized entities are exempt from this requirement, and un-audited financial statements suffice for these smaller companies.
The auditor, appointed by the shareholders' meeting or, in case of default, by the board of directors, must provide an auditor's report that includes an assessment of whether the financial statements provide information in accordance with the accounting principles generally accepted in the UAE and accurately represent the company's financial position and results for the year.
Non-resident entities operating in Dubai should be aware of these audit thresholds and requirements to ensure compliance with UAE regulations. Consulting with legal and accounting professionals can help determine the appropriate course of action based on the company's size and specific circumstances.
Organizational Structure
Legal Structure and Registration
Tax Regulations
Operational Considerations
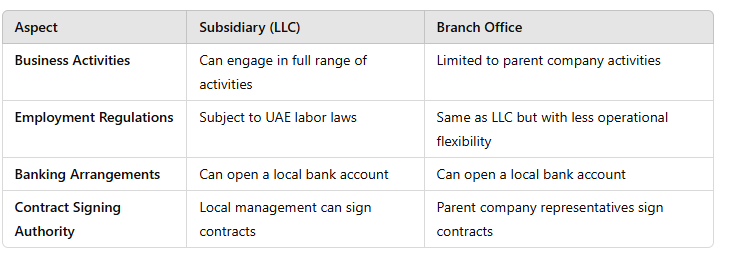
Compliance Requirements
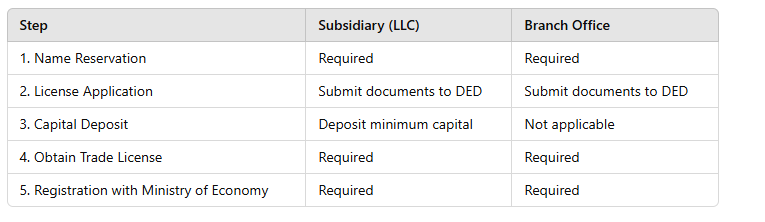
Establishment Process
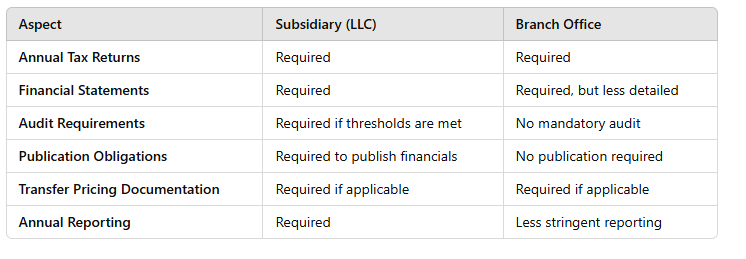
Estimated Costs
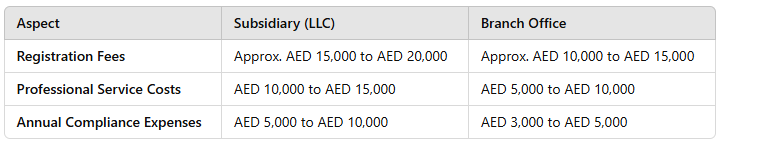
Tax Implications Comparison
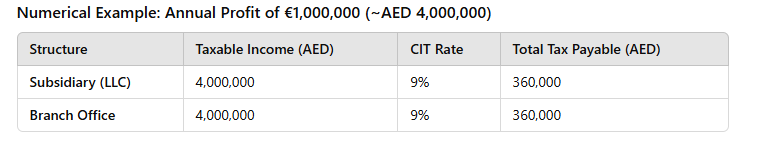
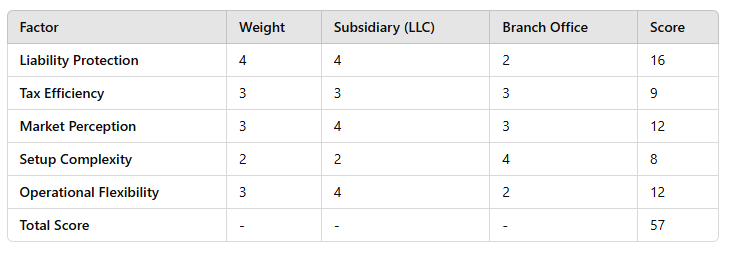
Decision Matrix
What types of taxes do businesses in Dubai need to file?
Businesses in Dubai primarily need to file Value Added Tax (VAT) returns, Corporate Tax returns (if applicable), and any other local fees or levies specific to their business activities.
How often do I need to file VAT returns?
VAT returns must typically be filed quarterly or annually, depending on your business’s turnover and the regulations set by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
What is the deadline for filing corporate tax returns in Dubai?
The deadline for filing corporate tax returns is generally nine months after the end of the financial year. However, it's essential to check specific guidelines based on your business's structure.
What documents do I need to prepare for tax filing?
Businesses need to prepare financial statements, VAT invoices, expense receipts, and any relevant tax registration documents. Additional documentation may be required for corporate tax filings.
Can I file my taxes online in Dubai?
Yes, businesses can file their VAT and corporate tax returns online through the Federal Tax Authority's (FTA) official portal or other designated online platforms.
Feel welcome, and try out our solutions and community,
to bring your business a step closer
to international expansion.
Got questions?
Lets talk about your options
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!